
Digital Servitization: how digital technology enables new business models
Davide Gamba currently serves as the Digital Business Innovation Partner at the Department of Digital Transformation, Information Systems, Security & Compliance for Gewiss SpA. His work involves applied research and innovation management in the digital business field. He holds a Ph.D. in Technology, Innovation, and Management from the University of Bergamo, focusing on servitization strategies, where he also teaches in digital innovation, strategic management, and information technology courses.
The transition to Industry 5.0 offers manufacturing companies like GEWISS new technological and business innovation opportunities, with increasing attention to sustainability and human-centricity.
Among the most promising levers is the servitization strategy, now enhanced by digital technologies.
Servitization: shifting the focus from product to product-service
Servitization can be defined as a strategy aimed at transforming the business model by shifting the focus from the product alone to Product-Service Systems (PSS), which can generate greater use value. In essence, it means moving from a transactional approach(selling the product) to a functional one (selling the function or outcome).
This transformation is neither immediate nor clear-cut, but rather takes the form of an evolutionary continuum, turning a company from a "pure-product provider" into a "pure-service provider.
"It’s noteworthy that servitization is not a conceptually recent phenomenon in B2B companies. The first documented industrial case dates back to 1966, when Rolls Royce Aviation shifted from selling expensive aircraft turbines to selling flight hours through long-term contracts under its Total Care – Power by the Hour service.
However, what has changed significantly in the last decade is the increasing pressure felt by manufacturing companies due to the proliferation of competition among producers and the subsequent product commoditization.
In summary:
- Servitization is how manufacturing companies transform their business model from mere producers of goods to providers of integrated product-service solutions.
- The Product-Service System (PSS) is the output of the servitization process. It comprises a system of products, services, infrastructures and support networks that promote business models based on functional sales, with lower environmental impact than traditional models.
Transactional Sale
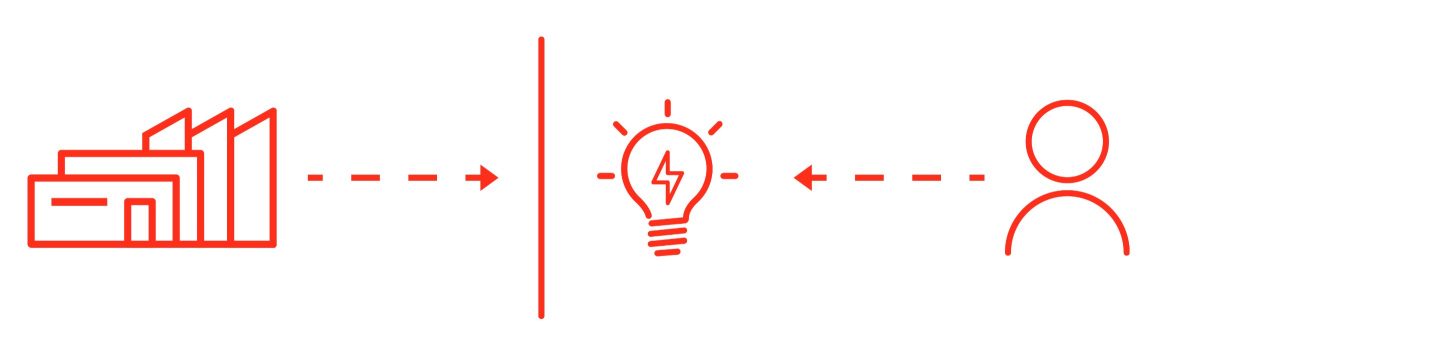
Functional Sale
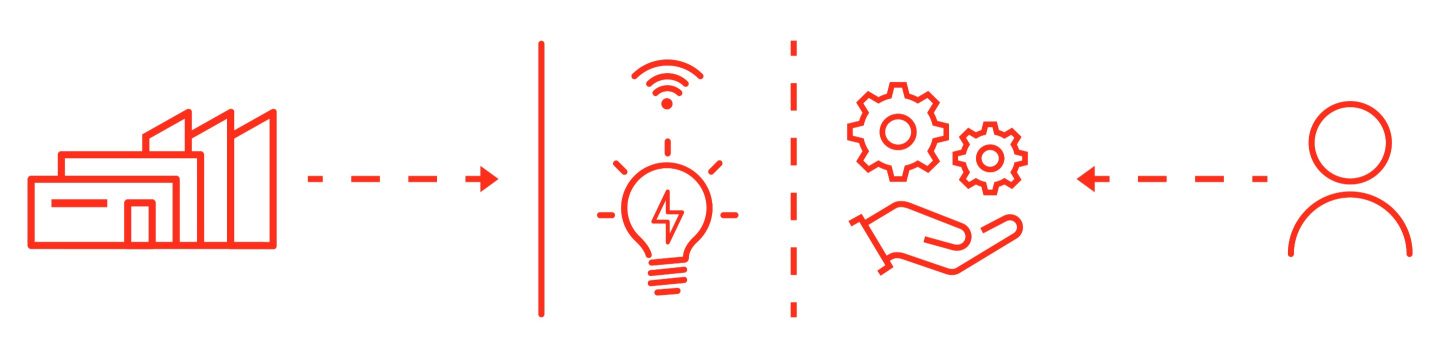
Digital servitization: the evolution enabled by technology
When the servitization strategy combines with the potential of digital technologies, it becomes digital servitization. Among the technologies that most allow this model, those used for collecting, storing, and leveraging data from installed products play a central role.
Specifically, we are referring to:
- Internet of Things (IoT): with sensors integrated into products, to collect real-time data on their usage and operational status.
- Cloud computing: through platforms that allow scalable storage and processing of the data collected from products.
- Big data analytics: using analytical tools to turn large volumes of data into valuable insights for strategic decisions and customized services.
Adopting digital servitization can bring multiple benefits to companies. By analyzing the data collected from connected products, it is possible to provide customized services, differentiate from competitors and generate recurring revenue streams over time. However, to realize these benefits it is essential to ensure product connectivity by adopting an IoT platform and a dedicated application – the so-called Digital Product-Service (DPS) – capable of effectively supporting the company’s data valorization strategy.
The DPS acts as the digital partner of PSS: it works alongside ERP and CRM systems to manage the processing and analysis of data from connected products. In this way, it enables the detection of events such as malfunctions or interventions, the identification of customer usage patterns and the activation of new operational workflows - such as the automatic reordering of spare parts. In addition, the system enables bidirectional communication with devices, allowing for remote management of commands, parameters and updates.
This integration between servitization strategy and digital technology enables the emergence of new servitized business models.
Servitized business models: XaaS
The Everything-as-a-Service (XaaS) business model originated in the Information Technology sector, particularly with the development of cloud computing. This approach offers resources such as infrastructures, applications and data on demand via the Internet.
Over time, the XaaS concept expanded beyond IT to the manufacturing sector. Here, digital technologies make it possible to access Product-Service Systems (PSS) flexibly and on request, paving the way for servitized business models.
The Pay-per-X model is the most distinctive feature of XaaS, as it radically changes the traditional revenue-generation mechanisms. This approach often involves defining complex contracts, requiring thorough negotiation between provider and client to clearly define usage conditions, payment methods and mutual responsibilities.
The result are new forms of collaboration built on trust and shared risk management, evolving into genuine strategic partnerships.Although XaaS has rapidly evolved in recent years, all its variations remain faithful to the as-a-service logic, which is consistent with the principles of servitization. In this new paradigm, the provider takes on part of the risks traditionally borne exclusively by the client – from financial and operational risks to end-user behavior.
This shift in perspective regarding the provision of PSS solutions also translates into new contractual frameworks, reflecting the various categories of XaaS models available today.
Digital servitization: a strategic opportunity for manufacturing companies
Ultimately, digital servitization offers tangible opportunities for companies aiming to evolve their business model and strengthen their leadership in the market. Enabled by digital technologies, the integration between products and services allows companies to sharpen their market differentiation and respond to customer needs with greater speed and personalization.
Furthermore, collecting and analyzing data from connected solutions through a DPS platform enables the company to anticipate market needs, optimize technical support and develop new business models based on recurring revenue.
Investing in digital servitization today means preparing to lead change, gradually building a solid and sustainable competitive advantage, fully aligned with the core principles of Industry 5.0.
Trending Topics
Show other categories



























